Is breast fibrosis dangerous? Breast fibrosis: causes and consequences of pathology, principles of treatment Diffuse fibrosis of the mammary glands
Throughout life, a woman’s mammary glands undergo many external and internal changes. One of these changes is the involution of the mammary glands, which occurs as the period of menopause approaches.
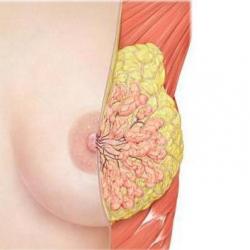
During this period, the glandular tissue of the breast is replaced by fatty tissue. But in addition to these two types, the mammary gland contains connective tissue cells - stroma. And there are often cases when, in addition to adipose tissue, excessive growth of connective tissue begins. This process is called fibrosis.
What it is
What is breast fibrosis? Another common name for this problem is mastopathy. These are pathological compactions or formations, which mainly consist of connective tissue made of collagen and elastin. Such a pathological process can form in any tissue of the body. It is benign in nature.

Causes
It should be noted that every year this disease affects an increasing number of women.
The reason for the uncontrolled growth of fibrous tissue in the mammary gland is mainly a hormonal imbalance, and all other factors are provoking:
- hormonal changes that occur during menopause, pregnancy and lactation;
- surgical interventions in the breast area;
- radiation therapy;
- the use of foreign bodies, for example, implants for breast augmentation;
- prolonged state of stress and overwork;
- diseases of the thyroid or pancreas;
- gynecological diseases, abortions, refusal to breastfeed, etc.;
- heredity.

Symptoms
At the initial stage of compaction formation, symptoms show little. Most often, this disease can be suspected by independently detecting one or more small ball-shaped lumps under the skin.
In the area of these formations there may be a slight change in skin color. Depending on the size of the compaction, a woman may experience a feeling of discomfort, heaviness and bloating. You may experience slight pain - nagging or aching, which can radiate, for example, to the shoulder. With obvious fibrosis, lymph nodes may become enlarged.
This pathology is often distinguished from other diseases by the absence of nipple discharge.

Kinds
There are several types of fibrosis depending on the location or method of location, as well as the cells involved in the proliferation process.
Local (focal)
This type of fibrosis is very common. And many women are interested in what “local fibrosis” is and is it dangerous? This type is characterized by the concentration of compaction at one point. Most often, such lumps appear in the upper parts of the chest. Local fibrosis of the mammary gland is what the onset of breast disease usually looks like. If you miss this moment, then more serious violations may develop. The downside is that a small seal is extremely difficult to detect. Usually it can only be felt when it reaches a certain size.
The detected focal fibrosis of the mammary gland is benign. But, nevertheless, focal fibrosis of the mammary gland requires treatment without fail. Inaction is fraught with uncontrolled growth of connective tissue, which in the future will lead to diffuse fibrosis.

Diffuse
Diffuse fibrosis of the mammary gland differs from focal fibrosis in that the spread of connective tissue does not affect a single gland, but the entire breast tissue. The formations can be large and it is quite difficult to cure this form.
It is accompanied by various unpleasant symptoms: pain, swelling, discharge from the nipples, etc. If treatment is not started in a timely manner, this will lead to surgery.

Stromal fibrosis
The stroma is part of the connective tissue of the mammary gland. The peculiarity of fibrosis of the mammary gland stroma is that as it grows, voids are formed that are filled with fluid.
Breast stromal fibrosis is quite harmless, but has unpleasant symptoms that can affect a woman’s general well-being. Treatment of focal stromal fibrosis is prescribed individually, after additional examination.

Periductal
Another obscure diagnosis that raises questions: periductal fibrosis of the mammary gland - what is it? It is also called plasmacytic, as it is characterized by the appearance of collagen fibers, which is part of the connective tissue, around the milk ducts.
Most often, this form is observed in women during menopause.
Linear
Linear fibrosis of the mammary gland has the additional names “interlobular” or “stranded” fibrosis. This is the result of proliferation of interlobular connective and intraductal tissue, which is often accompanied by the formation of cysts. This process is clearly visible in the photographs and is felt upon palpation by a specialist.

Diagnostics
One of the first forms of diagnosing breast fibrosis is an independent examination of the breast by palpation. If suspicious symptoms appear, you should immediately contact a specialist. He will conduct an initial examination and analysis of complaints. If necessary, some types of additional studies may be prescribed.
First of all, the following is carried out:
- Ultrasound and mammography;
- blood test for hormones and general clinical analysis.

To determine the nature of the formations and clarify the diagnosis, the following can be used:
- CT scan;
- Doppler sonography – assessment of blood circulation;
- biopsy;
- chropoductography - X-ray with contrast of the ducts of the mammary glands.

Treatment
The chosen type of treatment for breast fibrosis directly depends on the detected form, the degree of neglect of the disease, as well as the individual characteristics of the body, for example: age, past gynecological diseases, etc.

Conservative
Preference is given to conservative treatment methods. It is suitable for almost all forms of breast fibrosis that are in the initial stages of their development. First of all, the hormonal background is examined, and treatment with hormonal drugs is prescribed.
In addition, homeopathic remedies are used, for example, to treat diffuse fibrous formation in the mammary gland.

Surgical
Surgical intervention is prescribed as a last resort, and only in cases where nodular fibrosis of the mammary gland or large cystic formations are detected.

Forecast
Almost 30% of women who are diagnosed with lumps of various kinds are diagnosed with breast fibrosis. This disease is not a pathology leading to oncology. But it is necessary to undergo constant examinations and treatment, since the likelihood of developing a serious illness is much higher than in women with healthy breasts.
A diagnosis such as breast fibrosis is not very scary and is diagnosed in many women. But it obliges you to monitor the condition of the mammary glands even more carefully than before.
Video
You will learn about the symptoms, causes and treatment of mastopathy from our video.
Fibrous tissue is a type of connective tissue consisting of collagen and elastic fibers that provide relatively high tensile strength. Mechanical injuries and inflammatory processes occurring in the body contribute to its growth and activation of collagen production, which leads to the formation of nodes and tissue compaction (fibrosis). In women, this pathology mainly develops in the mammary glands.
Reasons for development
With the development of an inflammatory process or mechanical damage, fibroblasts are activated to isolate healthy membranes from infection or hemorrhage. They accelerate the production of collagen, elastin and glycoprotein cells, which are the basis of connective tissue. This process can occur in all internal organs of a person.
More often, stromal fibrosis develops in women of childbearing and menopausal age in the mammary glands and uterus (myometrium). As a result of the pathological proliferation of connective tissue, the formation of compactions and scars, an inevitable disruption of the organ’s functioning occurs. Thus, fibrosis of the myometrial stroma is the cause of missed abortion and infertility.
The main reason for the development of the disease is a change in the level of hormones in the blood during pregnancy, lactation, menopause and as a result of natural or artificial abortion.
General factors leading to the replacement of organ cells with connective tissue include:
- genetic predisposition;
- diseases of the thyroid and pancreas;
- use of hormonal contraceptives (pills, intrauterine device);
- inflammatory processes in the uterus and ovaries;
- completing a training course (radiotherapy), hormonal therapy;
- early puberty;
- late pregnancy;
- mechanical damage to tissues;
- allergic reactions;
- bad habits;
- obesity;
- unfavorable environmental conditions;
- stressful situations.
In addition to the above reasons, the disease can occur due to refusal of breastfeeding.
Forms and symptoms
The breast is composed of fatty, glandular and fibrous tissue. With age, as reproductive function declines, fat cells are replaced by glandular ones. The main function of the stroma is to support their location, form the walls of the milk ducts and septa between the lobules of the parenchyma.
- With the development of mastopathy, the stroma grows and displaces glandular cells, which transform into cavities (cysts). If connective tissue predominates in the breast, fibrosis develops, the nature of which depends on the form of the pathology.
- At the initial stage of the disease, local fibrosis appears. This type is characterized by the formation of mobile (not fused to the skin) nodes (cysts) with clear contours and a smooth surface. They have a round shape and range in size from 0.2 cm to 3 cm. The lesions are easy to detect by palpation.
- If left untreated, connective tissue grows, displacing parenchyma and fat cells. Complete damage to the mammary gland is called extensive (diffuse) fibrosis. It does not have clear boundaries when palpated.
- Women of menopausal age often develop periductal fibrosis (plasmacytic). It is characterized by the growth of stroma around the milk ducts.
- In ductal fibrosis, excessive formation of connective tissue occurs inside the milk ducts, while adjacent tissues are not affected. It is a type of periductal form.
- Periductal perivascular fibrosis involves areas around the milk ducts, lymphatics and blood vessels.
- Excessive growth (proliferation) of interlobular connective and intraductal tissues is called linear (interlobular) fibrosis. When palpating the breast, dense cords are felt, the contours of which are clearly visible on the mammographic image.
Symptoms of breast fibrosis:
- the presence of moving nodes or compacted areas of different localization that do not cause pain upon palpation;
- change in skin pigmentation over the site of the gland lesion (not always found);
- liquid discharge from the nipple mixed with blood or clear;
- discomfort in the chest (pain, heaviness, pressure from inside);
- severe nagging pain during menstruation, radiating to the armpit and shoulder;
- swelling and engorgement of the mammary glands in the premenstrual period.
If cysts form during the growth of fibrous tissue, then when they are palpated, a feeling of pain appears; before the onset of menstruation, the lymph nodes may enlarge. As the disease progresses, the size of the nodes increases.
Depending on the strength of the manifestation of characteristic symptoms, the disease can be moderate or severe.
Diagnostics
To diagnose breast fibrosis, consultation with a mammologist and gynecologist is necessary. During the conversation, the specialist finds out the presence of a genetic predisposition to this pathology and chronic diseases, the date and nature of the last menstruation, and whether hormonal medications are being taken, including for the purpose of contraception.
After palpation of the chest, additional examinations are prescribed:
- general blood analysis;
- mammography;
- blood test for hormone levels;
- Ultrasound of the mammary glands and pelvic organs;
- Doppler sonography - study of the blood vessels located in the mammary glands and the movement of blood through them;
- X-ray of ducts using a contrast agent (chromoductography);
- taking a puncture from neoplasms and its cytological examination;
- computed tomography and MRI.
If the presence of neoplasms is confirmed, then consultation with an oncologist is necessary, since women with fibrous changes in the mammary glands are at risk of developing breast cancer.
Treatment
Once fibrosis is diagnosed, treatment should not be delayed. Depending on the severity of the pathology, surgical or conservative methods are used for treatment. In the initial stages, the disease responds well to drug treatment.
When choosing tactics, the reasons for the development of the disease, the patient’s age, the presence of inflammatory processes, chronic diseases, disorders in the functioning of the endocrine organs and the central nervous system are taken into account.
- Focal stromal fibrosis and other forms of pathology require hormonal therapy. Proliferation of connective tissue is stimulated by estrogen. The activity of this process can be blocked by progesterone. Progesterone deficiency in the body is accompanied by the appearance of swelling of the mammary glands and hypertrophy of intralobular fibrous tissue, which leads to the formation of cysts. To normalize the balance, drugs containing progesterone (Duphaston) and tamoxifen (Cytofen), which neutralize the effect of estrogen, are prescribed.
- For local treatment of fibrosis of the mammary glands, progesterone-containing gel Progestogel is used. It has an analgesic effect and relieves swelling.
- Mastopathy can develop against the background of increased levels of prolactin in the blood. In this case, drugs are prescribed that reduce the production of the hormone (Ronalin, Bromocriptine).
- Extensive breast fibrosis is treated using the homeopathic remedy Mastodinon.
- If there are problems with the thyroid gland, medications containing iodine are prescribed.
- In case of severe swelling, it is necessary to take herbal diuretics.
- Fibrosis cannot be treated without the use of vitamin-mineral complexes and sedatives.
If conservative treatment is ineffective, as well as in the later stages of fibrosis development, surgical intervention is necessary. To remove formed nodes and cysts, sectoral resection or enucleation is performed (husking out benign neoplasms without removing adjacent healthy tissue). In rare cases, the breast must be completely amputated.
Prevention
It is impossible to completely exclude the possibility of developing fibrosis, but there are a number of recommendations, the implementation of which will reduce the risk of the appearance and recurrence of the pathology.
- During treatment for fibrosis, it is necessary to follow a special diet to maintain normal bowel function. It involves limiting the diet of animal fats and consuming large amounts of fiber found in vegetables, fruits and cereals.
- The use of hormonal drugs and contraception should be under the supervision of a physician and in compliance with the prescribed dosage.
- After the baby is born, it is advisable to breastfeed until milk is produced (at least 6 months).
Fibrosis is a protective reaction of the body in which connective tissue displaces fat and glandular cells in order to isolate the source of inflammation or hemorrhage. At the initial stage of development, the pathology practically does not manifest itself. Neoplasms (nodules, cysts) formed as a result of stromal hyperplasia are benign in nature, but there are cases of their degeneration into a malignant tumor. To prevent the development of severe complications, it is necessary to be regularly examined by a mammologist and gynecologist.
What is fibrosis? This is a disease of the mammary gland, which is characterized by an inflammatory process that provokes the formation of nodes and cysts. Every year there is an increase in incidence.
Causes of the disease
The development of the disease is influenced by many factors: refusal of childbearing and breastfeeding, poor lifestyle, early puberty, late menopause.
These factors lead to an increase in the production of estrogen; in addition, they provoke the body’s excessive sensitivity to the slightest fluctuations in hormonal balance.
Breast fibrosis varies depending on the type of course:
- Focal (local) breast fibrosis. This form of pathology is characterized by the appearance of pathological foci in which cysts and nodes develop. In addition, in medicine this form is considered the initial stage of fibrosis. At this period of development, the disease is easy to diagnose through a routine examination;
- Diffuse (extensive) breast fibrosis. In this case, we are talking about the progression of the disease, when the pathological process affects absolutely the entire gland. Characterized by complete destruction of the glandular tissue of the breast.
Symptoms of breast disease
- Availability of seals;
- Change in skin color;
- Nipple discharge;
- Feeling of heaviness, fullness, pain.
Stromal fibrosis in breast tissue
In this case, we are talking about the pathological growth of one’s own fibrous tissue – the stroma, which supports and connects adipose tissue and parenchyma.
Also, through the fatty tissues of the breast, there are peculiar partitions of fibrous tissue that connect the skin with the glandular capsule.
Periductal (plasmacytic) fibrosis of the mammary gland
This form of the disease is characterized by the formation of collagen fibers around the milk ducts. This type is mainly found in menopausal women.
A type of pathology is dictal fibrosis - damage to the ducts that does not affect other breast tissues. The periductal perivascular appearance is characterized by excessive growth of connective tissue around ducts, lymphatics and blood vessels.
Linear (interlobular, stranded) fibrosis of the mammary gland
This form of pathology occurs as a result of proliferation of interlobular connective and intraductal tissue. Cysts often form in this case. On palpation, dense cords are detected in the chest. Linear fibrosis with cords is clearly visible on mammography.
Diagnostics
- Palpation (palpation) of the chest, regional lymph nodes;
- Mammography – radiography of the mammary glands;
- General blood test, as well as a study of hormone levels;
- Doppler sonography – study of the state of blood vessels and blood flow;
- Chromoductography - x-ray of ducts with the introduction of contrasts;
- Biopsy and further histological examination of the obtained biological materials.
Treatment of breast fibrosis
After confirmation of the diagnosis, therapy begins immediately, without delay. Timely contact with a specialist plays an important role. You should consult a doctor if the slightest alarming signs appear. Otherwise, complications will arise that are more serious than fibrosis itself.
- The doctor must conduct comprehensive diagnostics in order to accurately establish the diagnosis and identify the cause of the pathology, to obtain a complete clinical picture. Treatment can be conservative or surgical, depending on the severity of the disease.
- Female breasts in the presence of this pathology are not always subject to removal; surgical intervention involves excision of only cysts and nodes. It is worth noting that surgery is used extremely rarely., in very complex cases with an acute course. As a rule, the disease is well treated with conservative methods.
- As for the latter, a complex effect is implied, including eliminating the cause of the disease. Typically therapy includes diet, treatment of premenstrual syndrome and various hormonal medications.
- Treatment tactics are determined by the form of the detected disease and its etiology. The patient’s age, the presence of pelvic inflammation, and endocrine disorders are taken into account.
- Focal fibrosis, however, like other forms of the disease, requires taking hormonal drugs. For example, a doctor may prescribe progesterone (Duphaston) if it is deficient. Such a remedy will neutralize the effect of estrogens. As a rule, they drink it one tablet per day for 2 weeks in each menstrual cycle.
- Tamoxifen is an anti-estrogenic drug(“Cytofen”, “Zitazonium”), blocking endogenous estrogen receptors. It is prescribed for menopause, cancer of the endometrium, breast, and infertility due to unripe eggs.
- For external use, Progestogel is often prescribed. This product contains progesterone and relieves swelling. Sold in gel form and applied to the skin twice a day.
- Sometimes the doctor prescribes bromocriptine (“Parlodel”, “Abergin”) - a drug that limits the synthesis of somatropin and prolactin, but it is contraindicated for use in benign neoplasms and premenstrual syndrome.
- Diffuse fibrosis is often treated with the drug Mastodinon. The product refers to homeopathic and is an alcoholic tincture of several plants (iris, tiger lily, cyclamen, emetic). Take it 30 drops twice a day for 3 months.
- When identifying hypothyroidism and iodine deficiency, potassium iodide is prescribed(“Iodomarin, etc.). If there are problems with the liver, it is necessary to supplement therapy with hepatoprotectors (Essentiale, Karsil, etc.). The treatment complex includes vitamin therapy (B vitamins, as well as A, E and C).
- With severe swelling, there is a need for herbal diuretics.
- Typically, treatment is not complete without taking sedative (calming) drugs.
During therapy, it is necessary to maintain normal bowel function so that estrogens are not absorbed back into the blood, since at this time they are carefully eliminated by the liver. For these purposes, it is recommended to exclude animal fats from the menu and introduce more plant fiber (fruits, vegetables). It is worth noting that various folk remedies are useless in this case. Alkaloids, phytoncides and flavonoids will not be able to cope with such a disease.
What is fibrosis? This is a disease of the mammary gland, which is characterized by an inflammatory process that provokes the formation of nodes and cysts. The incidence rate is increasing throughout the year.
Causes of the disease
The development of the disease is influenced by a lot of factors: refusal of childbearing and breastfeeding, poor lifestyle, early puberty, late menopause.
These factors lead to an increase in the production of estrogen; in addition, they provoke the body’s excessive susceptibility to the slightest fluctuations in hormonal balance.
Breast fibrosis varies depending on the type of course:
- Focal (local) fibrosis of the mammary gland. This form of pathology is characterized by the origin of pathological foci in which cysts and nodes progress. In addition, in medicine this form is considered the initial stage of fibrosis. During this formative period, the disease is easy to diagnose through a routine examination;
- Diffuse (extensive) fibrosis of the mammary gland. In this case, we are talking about the progression of the disease, when the pathological process certainly affects the entire gland. Characterized by complete destruction of the glandular tissue of the breast.
Symptoms of breast disease
- Presence of seals;
- Change in skin color;
- Nipple discharge;
- Feeling of heaviness, fullness, pain.
Stromal fibrosis in breast tissue
In this case, we are talking about the pathological growth of one’s own fibrous tissue – the stroma, which supports and unites adipose tissue and parenchyma.
Also, original fibrous tissue septa pass through the fatty tissues of the breast, which connect the skin with the glandular capsule.
Periductal (plasmacytic) fibrosis of the mammary gland
This form of the disease is characterized by the formation of collagen fibers around the milk ducts. This type is mainly found in menopausal women.
A type of pathology is dictal fibrosis - damage to the ducts that does not affect other breast tissues. The periductal perivascular appearance is characterized by excessive growth of connective tissue around the ducts, lymphatics and blood vessels.
Linear (interlobular, stranded) fibrosis of the mammary gland
This form of pathology appears as a result of proliferation of interlobular connective and intraductal tissue. Often, cysts form. On palpation, dense cords are detected in the chest. Linear fibrosis with cords is clearly visible on mammography.
Diagnostics
- Palpation (palpation) of the chest, regional lymph nodes;
- Mammography – radiography of the mammary glands;
- A general overview of the blood, as well as a study of the level of hormones;
- Doppler sonography – examination of the condition of blood vessels and blood flow;
- Chromoductography - x-ray of ducts with the introduction of contrasts;
- Biopsy and subsequent histological examination of the obtained biological materials.
Treatment of breast fibrosis
After confirmation of the diagnosis, therapy begins immediately, without delay. Timely contact with an expert plays a significant role. You should consult a doctor if the slightest warning signs occur. Otherwise, complications will arise that are more important than the fibrosis itself.
The doctor must conduct a comprehensive diagnosis in order to correctly establish the diagnosis and identify the cause of the pathology, to obtain a complete clinical picture. Treatment can be conservative or surgical, depending on the severity of the disease.
Female breasts in the presence of this pathology are not always subject to removal; surgical tying involves excision of only cysts and nodes. It is worth noting that surgery is resorted to very rarely, in very difficult cases with an acute course. As usual, the disease can be easily treated with conservative methods.
As for the latter, a complex effect is implied, including eliminating the causes of the disease. Typically, therapy includes diet, treatment of premenstrual syndrome and various hormonal drugs.
Treatment tactics are determined by the form of the disease found and its etiology. The patient’s age, the presence of pelvic inflammation, and endocrine disorders are taken into account.
Focal fibrosis, however, like other forms of the disease, requires the use of hormonal drugs. For example, a doctor may prescribe progesterone (Duphaston) if there is a shortage of it. A similar remedy will neutralize the effect of estrogens. As usual, they drink it one tablet a day for 2 weeks in each menstrual cycle.
An anti-estrogenic drug is tamoxifen (“Cytofen”, “Zitazonium”), which blocks endogenous estrogen receptors. It is prescribed for menopause, cancer of the endometrium, breast, and infertility due to unripe eggs.
For external use, Progestogel is often prescribed. This product contains progesterone and relieves swelling. Sold in gel form and applied to the skin twice a day.
Sometimes the doctor prescribes bromocriptine (Parlodel, Abergin) - a drug that limits the synthesis of somatropin and prolactin, but it is contraindicated for use in benign neoplasms and premenstrual syndrome.
Diffuse fibrosis is often treated with the help of the drug Mastodinon. The remedy is classified as homeopathic and is an alcohol tincture of several plants (iris, tiger lily, cyclamen, emetic). Take it 30 drops twice a day for 3 months.
If hypothyroidism and iodine deficiency are detected, potassium iodide (Iodomarin, etc.) is prescribed. If there are problems with the liver, it is necessary to supplement therapy with hepatoprotectors (Essentiale, Karsil, etc.). The treatment complex includes vitamin therapy (B vitamins, as well as A, E and C).
With severe swelling, there is a need for herbal diuretics. Usually, treatment is not complete without taking sedative (calming) drugs.
During therapy, it is necessary to maintain typical bowel function so that estrogens are not absorbed back into the blood, because at this time they are carefully eliminated by the liver. For these purposes, it is recommended to exclude animal fats from the menu and introduce more plant fiber (fruits, vegetables). It is worth noting that various folk remedies are inappropriate in this case. Alkaloids, phytoncides and flavonoids will not be able to cope with such a disease.
I wish you health and great well-being!
Recently, mammologists are increasingly talking about an increase in the number of cases of breast fibrosis. The disease manifests itself in a benign growth of connective tissue of the breast - stroma. As a result, compactions are formed, which a woman often discovers by chance, only when examined by a doctor. And although breast fibrosis and treatment of the stroma is considered a harmless disease, it must be started immediately after detection, since any tumors in the breast can develop over time into a malignant tumor, as well as lead to cosmetic defects and psychological problems for the woman.
Speaking about such a diagnosis as stromal fibrosis, it is worth first talking in more detail about the structure of the mammary glands. The female breast consists of glandular and adipose tissue: the first forms the gland and ducts, the second gives the breast its shape. But between these two tissues there is a connective tissue that connects them. Also, fibrous tissue forms a kind of partitions that connect the skin with the glandular capsule. Connective tissue in the body is present not only in the chest - therefore the disease often affects the liver, prostate and thyroid glands, and even the lungs.
The even distribution of tissue in a woman’s breast is controlled by hormones, and with age, when fertility decreases, glandular tissue begins to be replaced by fatty tissue. When the hormonal balance (that is, the main regulator of the health of the female breast) is disturbed, the stroma begins to grow. Moreover, in its pure form, fibrosis is observed quite rarely, more often being one of the manifestations of another disease - fibrocystic mastopathy. In the early stages, it is extremely difficult to identify the disease, sometimes even impossible during examination. But gradually the fibrous tissue grows, forming nodes and compactions.
Formations that arise during fibrosis can be different, depending on the structure and location of the nodes:
- The local form is a round or oval formation with a smooth surface. It is easily determined by palpation and is mobile.
- Diffuse fibrosis is a more severe form and has another name - widespread. Connective tissue is intensively formed in and around the milk ducts. In this case, the growth does not have clear boundaries, and upon palpation it may not be detected.
- Severe or linear fibrosis occurs when tissue, growing inside the ducts and in the partitions between the lobules of the gland, forms elongated dense cords.
- Perivascular fibrosis manifests itself in excessive growth of connective tissue not only around ducts and septa, but also capillaries, blood and lymphatic vessels.

Causes and symptoms
As mentioned above, fibrosis of breast tissue manifests itself as a hormonal imbalance, so first of all it is necessary to find its cause. Experts divide the causes of hormonal instability into internal and external.
- Internal diseases include diseases of internal organs, injuries, termination of pregnancy, and refusal of breastfeeding.
- External causes include unhealthy environmental conditions, poor nutrition, bad habits, stress, and excessive physical activity.
Having determined the source of the imbalance, it is necessary to eliminate it or, at least, reduce the strength of its impact.
For breast fibrosis, treatment will always begin with various tests, nutritional correction and possibly even a special diet, giving up bad habits and an overly stressful lifestyle. Signs of the disease can be different and manifest differently in each woman.
Typically the most common ones include:
- Painful sensations, feeling of tension, discomfort
- Nipple discharge (clear)
- The appearance of lumps, nodules, changes in breast shape
- Changes in skin and nipple color
Remember that this list of symptoms can characterize many other diseases, including breast cancer, so you should not delay your visit to the doctor.

Diagnosis and treatment
The discovery of the slightest lump in a woman’s breast is an alarming sign that requires careful testing for malignancy. The thing is that surgical or drug intervention with an unspecified diagnosis can lead to an acceleration of cancer development.
Diagnosis of fibrosis has several stages:
- Examination by a mammologist, including palpation of the breast and tumors, as well as lymph nodes.
- Ultrasound and mammography. It is also possible that chromoductography (x-ray of the milk ducts with the introduction of contrasts) is necessary.
- Blood tests (general, hormone levels).
- Tissue biopsy, histological examination.
When the diagnosis is confirmed, the specialist will prescribe comprehensive treatment, focusing on the specifics of a particular case. Depending on the severity of the disease, both exclusively medicinal treatment and surgical treatment (up to the removal of a significant part of the breast) are possible. But it is important to note that they try to resort to operations less frequently, and usually they are limited only to the removal of nodes and cysts in the acute course of the disease. In most cases, doctors adhere to traditional methods of treatment.
Traditional or drug treatment usually includes the complex use of various hormonal drugs, homeopathic remedies and following special diets. The choice of hormonal drug will depend on whether the deficiency or excess of which hormone led to the development of the disease. Hormones can be taken both internally and externally - in the form of ointments. Homeopathic medicines can be prescribed, for example, for diffuse fibrosis.
In addition to the main treatment, vitamin complexes, iodine preparations, and sedatives are also included. Folk remedies - herbs, lotions, compresses - are ineffective, but can be used to alleviate some manifestations of the disease, however, under the strict supervision of a doctor.

Disease Prevention
Unfortunately, today it is impossible to completely prevent the development of the disease, so no woman is immune from it. However, as with any other breast disease. Therefore, mammologists recommend not to forget to conduct regular self-examination, the optimal time for which is the first two weeks of the menstrual cycle. Also, do not forget about scheduled visits to the gynecologist and mammologist, ultrasound examinations, and tests.
- First of all, they relate to childbearing; women who delay having a child until age 30 or later are much more likely to suffer from fibrosis.
- Women who abuse abortion and use of hormonal drugs are also at risk.
- A woman's refusal to breastfeed will also be an unfavorable factor.
And of course, as for the prevention of other diseases, you must try to lead a healthy lifestyle: fewer bad habits, more rest, healthy sleep and proper nutrition.
Hormonal levels affect many aspects of our health. It also supports the condition of the female breast, which reacts extremely sensitively to any violations. Breast fibrosis is one of the manifestations of hormonal imbalance, characterized by the proliferation of connective tissue.
The danger of the disease lies in the difficulty of identifying it in the early stages of development. Treatment of the disease in most cases involves only drug intervention, which, if the outcome is favorable, will allow you to get rid of the disease forever.